ABSTRACT:
The
field‐oriented control (FOC)
strategy of a permanent magnet synchronous motor (PMSM) in a simplified form is
based on PI‐type
controllers. In addition to their low complexity (an advantage for real‐time implementation),
these controllers also provide limited performance due to the nonlinear
character of the description equations of the PMSM model under the usual conditions
of a relatively wide variation in the load torque and the high dynamics of the
PMSM speed reference. Moreover, a number of significant improvements in the performance
of PMSM control systems, also based on the FOC control strategy, are obtained
if the controller of the speed control loop uses sliding mode control (SMC),
and if the controllers for the inner control loops of id and iq currents
are of the synergetic type. Furthermore, using such a control structure, very
good performance of the PMSM control system is also obtained under conditions
of parametric uncertainties and significant variations in the combined rotor‐load moment of inertia
and the load resistance. To improve the performance of the PMSM control system
without using controllers having a more complicated mathematical description,
the advantages provided by reinforcement learning (RL) for process control can
also be used. This technique does not require the exact knowledge of the mathematical
model of the controlled system or the type of uncertainties. The improvement in
the performance of the PMSM control system based on the FOC‐type strategy, both
when using simple PI‐type
controllers or in the case of complex SMC or synergetic‐type controllers, is
achieved using the RL based on the Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient (DDPG).
This improvement is obtained by using the correction signals provided by a
trained reinforcement learning agent, which is added to the control signals ud,
uq, and iqref. A speed observer is also implemented for
estimating the PMSM rotor speed. The PMSM control structures are presented
using the FOC‐type
strategy, both in the case of simple PI‐type
controllers and complex SMC or synergetic‐type
controllers, and numerical simulations performed in the MATLAB/Simulink
environment show the improvements in the performance of the PMSM control
system, even under conditions of parametric uncertainties, by using the RL‐DDPG.
KEYWORDS:
1. Permanent
magnet synchronous motor
2. Sliding
mode control
3. Synergetic
control
4. Reinforcement
learning
5. Deep neural networks
SOFTWARE: MATLAB/SIMULINK
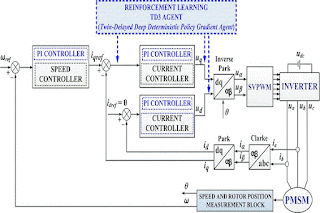
BLOCK DIAGRAM:
Figure 1. Block diagram for FOC‐type control of the
PMSM based on PI‐type
controllers using RL.
EXPECTED SIMULATION RESULTS:
Figure 2. Time evolution for the numerical
simulation of the PMSM control system based on the FOC‐type
strategy.
Figure 3. Time evolution for the numerical simulation
of the PMSM control system based on the RL‐TD3 agent for
the correction of iqref.
Figure 4. Time evolution for the numerical
simulation of the PMSM control system based on the
RL‐TD3
agent for the correction of udref and uqref.
Figure 5. Time evolution for the numerical
simulation of the PMSM control system based on the
RL‐TD3
agent for the correction of udref, uqref, and iqref.
Figure 6. Time evolution for the numerical
simulation of the PMSM control system based on control
using
SMC and synergetic controllers.
Figure 7. Time evolution for the numerical
simulation of the PMSM control system based on control
using
SMC and synergetic controllers using an RL‐TD3 agent for
the correction of iqref.
CONCLUSION:
This paper presents the FOC‐type control structure of a PMSM, which is improved in terms of performance by using a RL technique. Thus, the comparative results are presented for the case where the RL‐TD3 agent is properly trained and provides correction signals that are added to the control signals ud, uq, and iqref. The FOC‐type control structure for the PMSM control based on an SMC speed controller and synergetic current controller is also presented. To improve the performance of the PMSM control system without using controllers having a more complicated mathematical description, the advantages provided by the RL on process control can also be used. This improvement is obtained using the correction signals provided by a trained RL‐TD3 agent, which is added to the control signals ud, uq, and iqref. A speed observer is also implemented for estimating the PMSM rotor speed. The parametric robustness of the proposed PMSM control system is proved by very good control performances achieved even when the uniformly distributed noise is added to the load torque TL, and under high variations in the load torque TL and the moment of inertia J. Numerical simulations are used to prove the superiority of the control system that uses the RL‐TD3 agent.
REFERENCES:
1.
Eriksson, S. Design of Permanent‐Magnet
Linear Generators with Constant‐Torque‐Angle Control for Wave
Power. Energies 2019, 12,
1312.
2.
Ouyang, P.R.; Tang, J.; Pano, V. Position domain nonlinear PD control for
contour tracking of robotic manipulator. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 2018, 51, 14–24.
3.
Baek, S.W.; Lee, S.W. Design Optimization and Experimental Verification of
Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Used in Electric Compressors in Electric
Vehicles. Appl. Sci. 2020,
10, 3235.
4.
Amin, F.; Sulaiman, E.B.; Utomo, W.M.; Soomro, H.A.; Jenal, M.; Kumar, R.
Modelling and Simulation of Field Oriented Control based Permanent Magnet
Synchronous Motor Drive System. Indones. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 2017, 6, 387.
5.
Mohd Zaihidee, F.; Mekhilef, S.; Mubin, M. Robust Speed Control of PMSM Using
Sliding Mode Control (SMC)—A Review. Energies 2019, 12, 1669.