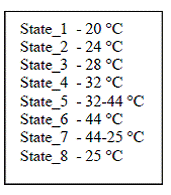
ABSTRACT:
The
changes in temperature and radiation cause visible fluctuations in the output
power produced by the photovoltaic (PV) panels. It is essential to keep the
output voltage of the PV panel at the maximum power point (MPP) under varying
temperature and radiation conditions. In this study, a maximum power point tracking
(MPPT) method has been developed which is based on mainly two parts: the first
part is adapting calculation block for the reference voltage point of MPPT and
the second one is Fuzzy Logic Controller (FLC) block to adjust the duty cycle
of PWM applied switch (MOSFET) of the DC-DC converter. In order to evaluate the
robustness of the proposed method, Matlab/Simulink program has been used to
compare with the traditional methods which are Perturb & Observe (P&O),
Incremental Conductance (Inc. Cond.) and FLC methods under variable atmospheric
conditions. When the test results are observed, it is clearly obtained that the
proposed MPPT method provides an increase in the tracking capability of MPP and
at the same time reduced steady state oscillations. The accuracy of the
proposed method is between 99.5% and 99.9%. In addition, the time to capture
MPP is 0.021 sec. It is about four times faster than P&O and five times
faster than for Inc. Cond. and, furthermore, the proposed method has been
compared with the conventional FLC method and it has been observed that the
proposed method is faster about 28% and also its efficiency is about 1% better
than FLC method.
KEYWORDS:
1. PV
2. MPPT
methods
3. FLC
based MPPT
4. DC-DC
converter
SOFTWARE: MATLAB/SIMULINK
BLOCK DIAGRAM:
Fig. 1. Block diagram of the designed system.
Fig. 2. PV currents for proposed MPPT technique.
Fig. 3. PV voltages for
proposed MPPT technique under variable irradiance (fixed temperature).
Fig. 5. PV currents for
proposed MPPT technique.
Fig. 6. PV voltages for
proposed MPPT technique under variable temperature (fixed irradiance).
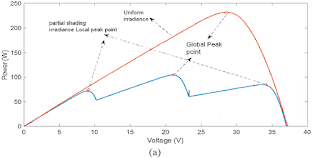
Fig. 7. (a) P-V characteristics curve, (b) Tracking global peak point for proposed MPPT technique.
CONCLUSION:
This
study proposes a novel MPPT method and the detailed performance comparison with
commonly used methods such as P&O, Incremental conductance and FLC techniques
is achieved. Under sudden change in atmospheric operating conditions, the
proposed MPPT method performs better performance than other methods to
determine MPP. The efficiency of proposed MPPT method is between 99.5% and
99.9%, while P&O is between 91% and 98%, Inc. Cond. Is between 96% and 99%
and FLC is between 98.8% and 99.4% for all case studies. The proposed MPPT
method has achieved the lowest oscillation rate at the MPP compared to commonly
used methods. This brings the method to the forefront in terms of efficiency.
The duration of the proposed MPPT technique to reach a steady state has been measured
as 0.021 sec. It is about four times faster than P&O and five times faster
than for Inc. Cond. and, furthermore, the proposed method has been compared
with the conventional FLC method and it has been observed that the proposed
method is faster about 28% than FLC method this means the speed of proposed
MPPT technique is the best. At the same time, the amount of oscillation is very
low compared to conventional methods. The accuracy of the algorithm is high
(%99.9 in many study cases) and also the proposed method is easy to implement in
the system.
REFERENCES:
[1]
Luo HY, Wen HQ, Li XS, Jiang L, Hu YH. Synchronous buck converter based lowcost
and high-efficiency sub-module DMPPT PV system under partial shading
conditions. Energy Convers Manage 2016;126:473–87.
[2]
Babaa SE, Armstrong M, Pickert V. Overview of maximum power point tracking control
methods for PV systems. J Power Energy Eng 2014;2:59–72.
[3]
Dolara AFR, Leva S. Energy comparison of seven MPPT techniques for PV systems.
J Electromagn Anal Appl 2009;3:152–62.
[4]
Ngan MS, Tan CW. A study of maximum power point tracking algorithms for
standalone photovoltaic systems. Applied Power Electronics Colloquium (IAPEC):
IEEE. 2011. p. 22–7.
[5]
Liu JZ, Meng HM, Hu Y, Lin ZW, Wang W. A novel MPPT method for enhancing energy
conversion efficiency taking power smoothing into account. Energy Convers Manage
2015;101:738–48.