ABSTRACT
This paper
deals with the analysis, design and control of a three-level 24-pulse Voltage
Source Converter (VSC) based High Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) system. A three
level VSC operating at fundamental frequency switching (FFS) is proposed with
24-pulse VSC structure to improve the power quality and reduce the converter
switching losses for high power applications. The design of three-level VSC
converter and system parameters such as ac inductor and dc capacitor is
presented for the proposed VSC based HVDC system. It consists of two converter
stations fed from two different ac systems. The active power is transferred
between the stations either way. The reactive power is independently controlled
in each converter station. The three-level VSC is operated at optimized dead
angle (β). A coordinated control algorithm for both the rectifier and an inverter
stations for bidirectional active power flow is developed based on FFS and
local reactive power generation. This results in a substantial reduction in
switching losses and avoiding the reactive power plant. Simulation is carried
to verify the performance of the proposed control algorithm of the VSC based HVDC
system for bidirectional active power flow and their independent reactive power
control.
KEYWORDS
Voltage Source
Converter (VSC), Three-level VSC, Fundamental Frequency Switching (FFS), HVDC
System, Power Flow Control, Reactive Power Control, Power Quality, Total
Harmonic Distortion (THD), Dead Angle (β).
SOFTWARE: MATLAB/SIMULINK
BLOCK DIAGRAM:
Fig.
1 Three-level 24-pulse double bridge VSC based HVDC system
EXPECTED SIMULATION RESULTS:
Fig.
2a Performance of rectifier station during reactive power control of three level
24-pulse VSC HVDC system
Fig.
2b Performance of Inverter station during reactive power control at rectifier
station of three-level 24 pulse VSC HVDC system
Fig.
2c Variation of (δ) and (α) values for rectifier and inverter Stations for reactive
power variation of a three-level 24-pulse VSC HVDC system
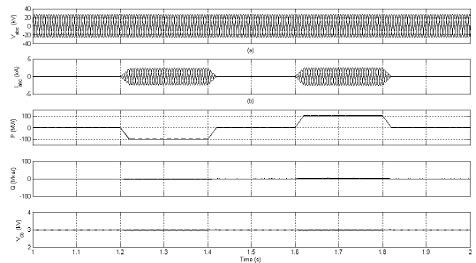
Fig.
3a Rectifier station during active power reversal of three-level 24-pulse VSC
HVDC system
Fig. 3b Inverter station during active
power reversal of three-level 24-pulse VSC HVDC system
Fig.
3c Variation of (δ) and (α) values during active power reversal of three level 24-pulse
VSC HVDC system.
CONCLUSION
A new three-level, 24-pulse voltage
source converter based HVDC system operating at fundamental frequency switching
has been designed and its model has been developed and it is successfully
tested for the independent control of active and reactive powers and acceptable
level harmonic requirements. The reactive power has been controlled independent
of the active power at both conditions. The converter has been successfully
operated in all four quadrants of active and reactive powers with the proposed
control. The reversal of the active power flow has been implemented by
reversing the direction of dc current without changing the polarity of dc voltage
which is very difficult in conventional HVDC systems. The power quality of the
HVDC system has also improved with three-level 24-pulse converter operation.
The harmonic performance of this three-level, 24-pulse VSC has been observed to
an equivalent to two-level 48-pulse voltage source converter.
REFERENCES
[1]
“It’s time to connect,” Technical description of HVDC Light Technology, ABB
HVDC Library.
[2] J. Arrillaga, “High Voltage Direct
Current Transmission,” 2nd Edition, IEE Power and Energy Series 29,
London, 1998.
[3] Vijay K. Sood, “HVDC and FACTS
Controllers - Applications of Static Converters in Power Systems,” Kluwer
Academic Publishers, Masachusetts, 2004.
[4] J. Arrillaga, Y. H. Liu and N. R.
Waston, “Flexible Power Transmission- The HVDC Options,” John Wiley &
Sons, Ltd, Chichester, UK, 2007.
[5] J. Arrillaga and M. E. Villablanca, “A
modified parallel HVDC convertor for 24 pulse operation,” IEEE Trans. on
Power Delivery, vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 231-237, Jan 1991.