ABSTRACT:
This paper proposes a sensorless speed control technique
for Brushless DC Motor (BLDC) drives by estimating speed from the hall sensor
signals. Conventionally, the speed is measured using precision speed encoders.
Since these encoders cost almost half of the entire drive system, there arises
the need for a low cost speed estimation technique. This is proposed by measuring
the frequency of the in-built-hall sensor signals. Here, a closed loop speed
control of BLDC motor is proposed using a current controlled pulse width
modulation (PWM) technique. Since BLDC motor is an electronically commutated machine,
the commutation period is determined by a switching table that shows the hall
signals’ status. The entire system was simulated in MATLAB/Simulink and the
performance of the system was analyzed for different speed and torque
references.
KEYWORDS:
1.
Brushless DC Motor (BLDC)
2.
Speed estimation
3.
Hall sensors
4.
Current controlled PWM
5.
Inverter
SOFTWARE: MATLAB/SIMULINK
BLOCK DIAGRAM:
Fig.1.
Proposed Block Diagram
EXPECTED SIMULATION RESULTS:
Fig.
2. Speed and Torque response of the BLDC drive for reference speed of 3000rpm;
(a) Speed; (b) Electromagnetic torque developed
Fig.
3. Speed and Torque response of the BLDC drive for reference speed of
2000rpm;
(a) Speed; (b) Electromagnetic torque developed
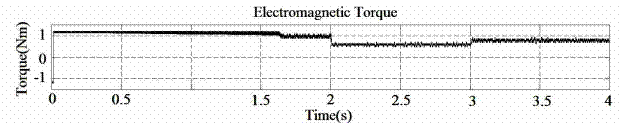
Fig.
4. Stator current measured for speed (reference) of 3000rpm and applied
torque
0.5Nm
Fig.
5. Back EMF measured for speed (reference) of 3000rpm and applied
torque
0.5Nm
Fig.
6. Speed and Torque response in sensored and sensorless mode for a reference
speed of 2500rpm; (a) Speed response in sensored mode; (b) Speed response in
sensorless mode; (c) Change in applied torques
CONCLUSION:
This
paper proposes a low cost speed estimation technique for BLDC motor drive. This
method was found to be working for the entire range of speeds below the rated
speed. The performance of the system was comparable with that of the conventional
speed encoder based control technique. Actual speed was found to maintain the
reference speed for different values of load torques. This was verified
successfully by using MATLAB/Simulink. Since the proposed speed estimation technique
does not require the motor parameters like resistance, inductance etc., the
system is suitable for robust applications, especially in industries.
The
future scope of the work can be extended as explained below:
•
Although the work emphasizes on speed encoder-less control technique, the cost
of the system can be further reduced by replacing the hall sensors with a
suitable low cost counterpart.
•
Since the torque-ripples are found to be appreciably high, novel techniques for
its reduction can be studied.
REFERENCES:
[1]
Hsiu-Ping Wang and Yen-Tsan Liu, “Integrated Design of Speed- Sensorless and
Adaptive Speed Controller for a Brushless DC Motor,” IEEE Transactions on
Power Electronics, Vol. 21, No. 2, March 2006.
[2]
K.S.Rama Rao, Nagadeven and Soib Taib, “Sensorless Control of a BLDC Motor with
Back EMF Detection Method using DSPIC,” 2nd IEEE International
Conference on Power and Energy, pp. 243-248, December 1-3, 2008.
[3]
W. Hong, W. Lee and B. K. Lee, “Dynamic Simulation of Brushless DC Motor Drives
Considering Phase Commutation for Automotive Applications,” Electric Machines
& Drives Conference,2007 lEMDC’07 IEEE International, , pp. 1377-1383, May
2007.
[4]
B. Tibor, V. Fedak and F. Durovsky, “Modeling and Simulation of the BLDC motor
in MATLAB GUI,” Industrial Electronics (lSIE), 2011 IEEE International
Symposium on Industrial Electronics, Gdansk, pp. 1403-1407, June 2011.
[5]
V. P. Sidharthan, P. Suyampulingam and K. Vijith, “Brushless DC motor driven
plug in electric vehicle,” International Journal of Applied Engineering
Research, vol. 10, pp. 3420-3424, 2015.