This
paper deals with a single stage solar powered speed sensorless vector
controlled induction motor drive for water pumping system, which is superior to
conventional motor drive. The speed is estimated through estimated stator flux.
The proposed system includes solar photovoltaic (PV) array, a three-phase
voltage source inverter (VSI) and a motor-pump assembly. An incremental
conductance (InC) based MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking) algorithm is
used to harness maximum power from a PV array. The smooth starting of the motor
is attained by vector control of an induction motor. The desired configuration
is designed and simulated in MATLAB/Simulink platform and the design, modeling
and control of the system, are validated on an experimental prototype developed
in the laboratory.
KEYWORDS:
1.
Speed Sensorless Control
2.
Stator Field-Oriented Vector Control
3.
Photovoltaic (PV)
4.
InC MPPT Algorithm
5.
Induction Motor Drive (IMD)
6.
Water Pump
SOFTWARE: MATLAB/SIMULINK
BLOCK DIAGRAM:
Fig. 1. PV fed induction motor drive configuration
Fig. 2. Starting and MPPT of PV array at 1000 W/m2
Fig. 3. Intermediate signals during starting at 1000 W/m2
(a)
(b)
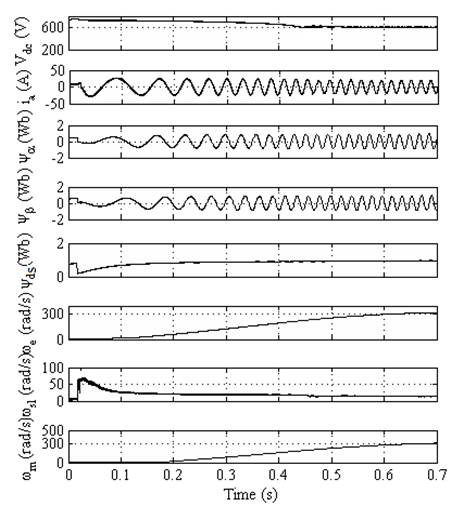
Fig. 4. Simulation results during starting at 1000 W/m2 (a)
Proposed drive (b) Waveforms showing sensed speed and estimated speed
Fig. 5. SPV array performance during decrease in insolation from 1000
W/m2 to 500 W/m2
(a)
(b)
Fig. 6. Dynamic performance during irradiance decrement from 1000 W/m2
to 500 W/m2 (a) Proposed drive (b) Waveforms showing sensed speed
and estimated speed
Fig. 7. PV array performance on increasing insolation from 500 W/m2
to 1000 W/m2
(a)
(b)
Fig. 8. Dynamic performance during irradiance decrement from 500 W/m2
to 1000 W/m2 (a) Proposed drive (b) Waveforms showing sensed speed
and estimated speed
CONCLUSION:
A
single stage solar PV array fed speed sensorless vector-controlled induction
motor drive has been operated subjected to different conditions and the steady
state and dynamic behaviors have been found quite satisfactory and suitable for
water pumping. The torque and stator flux, have been controlled independently.
The motor is started smoothly. The reference speed is generated by DC link
voltage controller controlling the voltage at DC link along with the speed
estimated by the feed-forward term incorporating the pump affinity law. The
power of PV array is maintained at maximum power point at the time of change in
irradiance. This is achieved by using incremental-conductance based MPPT
algorithm. The speed PI controller has been used to control the q-axis current
of the motor. Smooth operation of IMD is achieved with desired torque profile
for wide range of speed control. Simulation results have displayed that the
controller behavior is found satisfactory under steady state and dynamic
conditions of insolation change. The suitability of the drive is also verified
by experimental results under various conditions and has been found quite apt
for water pumping.
REFERENCES:
[1] R. Foster, M. Ghassemi and M. Cota, Solar energy: Renewable energy
and the environment, CRC Press, Taylor and francis Group, Inc. 2010.
[2] M. Kolhe, J. C. Joshi and D. P. Kothari, “Performance analysis of a
directly coupled photovoltaic water-pumping system”, IEEE Trans. on Energy
Convers., vol. 19, no. 3, pp. 613-618, Sept. 2004.
[3] J. V. M. Caracas, G. D. C. Farias, L. F. M. Teixeira and L. A. D. S.
Ribeiro, “Implementation of a high-efficiency, high-lifetime, and low-cost
converter for an autonomous photovoltaic water pumping system”, IEEE Trans.
Ind. Appl., vol. 50, no. 1, pp. 631-641, Jan.-Feb. 2014.
[4] R. Kumar and B. Singh, “ Buck-boost converter fed BLDC motor for
solar PV array based water pumping, ” IEEE Int. Conf. Power Electron. Drives
and Energy Sys. (PEDES), 2014.
[5] Zhang Songbai,
Zheng Xu, Youchun Li and Yixin Ni, “Optimization of MPPT step size in
stand-alone solar pumping systems,” IEEE Power Eng. Society Gen. Meeting, June
2006.