Dynamic Behavior of DFIG Wind
Turbine Under Grid Fault Conditions
ABSTRACT:
The use of doubly fed induction generators (DFIGs)
in wind turbines has become quite common over the last few years. These
machines provide variable speed and are driven with a power converter which is
sized for a small percentage of the turbine-rated power. This paper presents a
detailed model of induction generator coupled to wind turbine system. Modeling
and simulation of induction machine using vector control computing technique is
done. DFIG wind turbine is an integrated part of distributed generation system.
Therefore, any abnormalities associates with grid are going to affect the
system performance considerably. Taking this into account, the performance of DFIG
variable speed wind turbine under network fault is studied using simulation
developed in MATLAB/SIMULINK.
KEYWORDS
1. DFIG
2. DQ
Model
3. Vector Control
SOFTWARE: MATLAB/SIMULINK
BLOCK DIAGRAM:
Fig.
1 Simulink model of DFIG system
EXPECTED SIMULATION RESULTS:
Time (sec)
Fig. 2 Stator currents during balance
condition
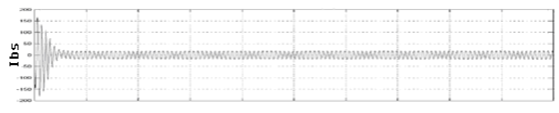
Fig.
3 Rotor currents during balance condition
Time (sec)
Fig.
4 Speed and torque during balance condition.
Time (sec)
Fig.
5 Acive and reactive power during balance condition
CONCLUSION:
This
paper presents a study of the dynamic performance of variable speed DFIG
coupled with wind turbine. The dynamic behavior of DFIG under power system
disturbance was simulated using MATLAB/SIMULINK.Accurate transient simulations
are required to investigate the influence of the wind power on the power system
stability. The DFIG considered in this analysis is a wound rotor induction generator
with slip rings. The stator is directly connected to the grid and the rotor is
interface via a back to back power converter. Power converter are usually
controlled utilizing vector control techniques which allow the decoupled
control of both active and reactive power flow to the grid. In the present investigation,
the dynamic DFIG performance is presented for both normal and abnormal grid
conditions. The control performance of DFIG is satisfactory in normal grid
conditions and it is found that, both active and reactive power maintains a study
pattern in spite of fluctuating wind speed and net electrical power supplied to
grid is maintained constant.
REFERENCES:
[1]
T. Brekken, and N. Mohan, “A novel doubly-fed induction wind generator control
scheme for reactive power control and torque pulsation compensation under
unbalanced grid voltage conditions”, IEEE PESC Conf Proc., Vol 2, pp. 760-764,
2003.
[2]
L. Xu and Y. Wang, “Dynamic modeling and control of DFIG-based wind turbines
under unbalanced network conditions”, IEEE Trans. On Power System, Vol 22,
Issues 1, pp. 314-323, 2007.
[3]
F.M. Hughes, O. Anaya-Lara, N. Jenkins, and G. Strbac, “Control of DFIG based
wind generation for power network support”, IEEE Trans. On Power Systems, Vol
20, pp. 1958-1966, 2005.
[4]
S. Seman, J. Niiranen, S. Kanerva, A. Arkkio, and J. Saitz, “Performance study
of a doubly fed wind-power induction generator Under Network Disturbances”,
IEEE Trans. on Energy Conversion, Vol 21, pp. 883-890, 2006.
[5]
T. Thiringer, A. Petersson, and T. Petru, “Grid disturbance response of wind
turbines equipped with induction generator and doubly-fed induction generator”,
in Proc. IEEE Power Engineering Society General Meeting, Vol 3, pp. 13-17,
2003.