ABSTRACT:
This paper proposes an adaptive and optimal control strategy
for a solar photovoltaic (PV) system. The control strategy ensures that the
solar PV panel is always perpendicular to sunlight and simultaneously operated
at its maximum power point (MPP) for continuously harvesting maximum power. The
proposed control strategy is the control combination between the solar tracker (ST)
and MPP tracker that can greatly improve the generated electricity from solar
PV systems. Regarding the ST system, the paper presents two drive approaches
including open- and closed-loop drives. Additionally, the paper also proposes
an improved incremental conductance algorithm for enhancing the speed of the MPP
tracking of a solar PV panel under various atmospheric conditions as well as
guaranteeing that the operating point always moves toward the MPP using this
proposed algorithm. The simulation and experimental results obtained validate
the effectiveness of the proposal under various atmospheric conditions.
KEYWORDS:
1.
Maximum power
point tracker (MPPT)
2.
Solar tracker (ST)
3.
Solar PV panel
SOFTWARE: MATLAB/SIMULINK
Fig.
1. Block diagram of the experimental setup.
EXPECTED SIMULATION RESULTS:
Fig.
2. Description of the variations of the solar irradiation and temperature.
Fig.
3. Obtained maximum output power with the P&O and improved InC algorithms
under the variation of the solar irradiation.
Fig.
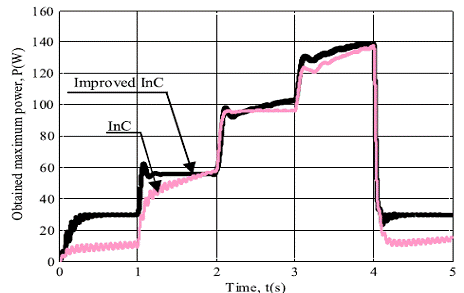
4. Obtained maximum output power with the InC and improved InC algorithms under
the variation of the solar irradiation.
Fig.
5. Obtained maximum output power with the P&O and improved InC algorithms
under both the variations of the solar irradiation and temperature.
Fig.
6. Obtained maximum output power with the InC and improved InC algorithms under
both the variations of the solar irradiation and temperature.
Fig.
7. MPPs of the solar PV panel under the variation of the solar irradiation
Fig.
8. MPPs of the solar PV panel under both the variations of the solar irradiation
and temperature.
Fig.
9. Experimental result of obtained maximum output power with the improved InC
algorithm under the variation of the solar irradiation.
CONCLUSION:
It
is obvious that the adaptive and optimal control strategy plays an important
role in the development of solar PV systems. This strategy is based on the combination
between the ST and MPPT in order to ensure that the solar PV panel is capable
of harnessing the maximum solar energy following the sun’s trajectory from dawn
until dusk and is always operated at the MPPs with the improved InC algorithm.
The proposed InC algorithm improves the conventional InC algorithm with an
approximation which reduces the computational burden as well as the application
of the CV algorithm to limit the search space and increase the convergence
speed of the InC algorithm. This improvement overcomes the existing drawbacks
of the InC algorithm. The simulation and experimental results confirm the
validity of the proposed adaptive and optimal control strategy in the solar PV panel
through the comparisons with other strategies.
REFERENCES:
[1]
R. Faranda and S. Leva, “Energy comparison of MPPT techniques for PV systems,” WSES
Trans. Power Syst., vol. 3, no. 6, pp. 446–455, 2008.
[2]
X. Jun-Ming, J. Ling-Yun, Z. Hai-Ming, and Z. Rui, “Design of track control
system in PV,” in Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Softw. Eng. Service Sci., 2010,
pp. 547–550.
[3]
Z. Bao-Jian, G. Guo-Hong, and Z. Yan-Li, “Designment of automatic tracking
system of solar energy system,” in Proc. 2nd Int. Conf. Ind. Mechatronics
Autom., 2010, pp. 689–691.
[4]
W. Luo, “A solar panels automatic tracking system based on OMRON PLC,” in Proc.
7th Asian Control Conf., 2009, pp. 1611–1614.
[5]
W. Chun-Sheng,W. Yi-Bo, L. Si-Yang, P. Yan-Chang, and X. Hong-Hua, “Study on
automatic sun-tracking technology in PV generation,” in Proc. 3rd Int. Conf.
Elect. Utility Deregulation Restruct. Power Technol., 2008, pp. 2586–2591.