ABSTRACT:
Now-a-days, sensorless speed control modes of operation are
becoming standard solutions in the area of electric drives. The technological
developments require a compact and efficient drive to meet the challenging
strategies in operation of the system. This paper provides a speed sensorless
control of an Induction motor with a model based adaptive controller with
stator current vectors. The purpose of the proposed control scheme is to create
an algorithm that will make it possible to control induction motors without
sensors. A closed loop estimation of the system with robustness against parameter
variation is used for the control approach. A Model Reference Adaptive System
(MRAS) is one of the major approaches used for adaptive control. The MRAS
provides relatively easy implementation with a higher speed adaptation algorithm.
MRAS proposed in this paper owing to its low complexity and less computational
effort proposes a feasible methodology to control the speed of an Induction
Motor (1M) drive without using speed sensors. Simulations results validate the
effectiveness of this technique.
KEYWORDS:
1.
Indirect Field oriented
control
2.
Induction motor drive
3.
Sensorless speed
estimation
4.
Model Reference Adaptive control.
SOFTWARE: MATLAB/SIMULINK
BLOCK DIAGRAM:
Fig.1.
Proposed Block Diagram of MRAS based 1M drive using
PI controller.
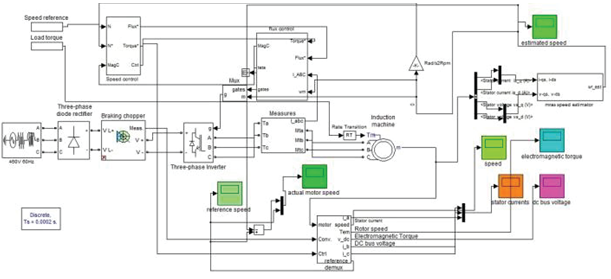
Fig.2.
Overall Simulink model of sensorless control of
induction motor using MRAS with PI controller.
EXPECTED SIMULATION RESULTS:
CONCLUSION:
The model based control scheme is basically an adaptive control
mechanism. The reference model of the proposed system consists of the response
to be obtained for the input conditions. The adaptive mechanism continuously monitors
the adaptable parameter (speed in this case). The
adaptable parameter is continuously subjected to changes based
on its deviation obtained by comparing it with the response of the reference
model. The speed estimation algorithm in MRAS is computationally less
intensive. MRAS is a relatively simple algorithm and hence less sophisticated
processing can be employed. MRAS strategy is more robust than the conventional
one. This makes it better suited if the drive is to be operated in hostile environments.
Owing to less sophisticated processing requirements, MRAS technique costs
cheaper and hence overall cost of the drive is reduced. With lower cost and greater
reliability without mounting problems, the sensorless vector control schemes
have made remarkable developments in electric drive technology. Due to lesser rise
time taken by MRAS, this method gives faster steady state response and this
scheme has better reliability than the conventional scheme.
REFERENCES:
[I] Teresa Orlowska - Kowalska and Mateusz Dybkowski ,
"Stator Current based MRAS estimator for a wide range speed Sensor less induction
motor drives", IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics vo1.51, No. 4,
April 2010, pp. 1296 - 1308.
[2] B. K. Bose, Power Electronics and Motor Drives, Pearson Education
Inc., Delhi, India, 2003.
[3] M. Rodic and K. Jezernik, "Speed-sensorless
sliding-mode torque control of induction motor," IEEE Transactions on
Industrial Electronics, vol. 49, no. I, pp. 87-95, February 2002.
[4] L. Harnefors, M. Jansson, R. Ottersten and K. Pietilainen, "Unified
sensorless vector control of synchronous and induction motors," IEEE
Transactions on Industrial Electronics, vol. 50, no.
1, pp. 153-160, February 2003.
[5] M. Comanescu and L. Xu, "An improved flux observer
based on PLL frequency estimator for sensorless vector control of induction motors,"
IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, vol. 53, no. 1, pp. 50-56,
February 2006.