Among the different disturbances affecting
the power quality, the voltage sag are considered as a most important power
quality problem faced by utilities, industrial consumer & equipment like
PLC (Programmable Logic Controller), ASD (Adjustable Speed Drives) which need
to be fully investigated. Custom power device are effective means for
mitigating the voltage related issues prominently voltage sag, unbalanced load
voltage, voltage regulation, sag/ swell etc. by compensating the reactive power
with the injection of shunt current. Various DSTATCOM topologies & control
scheme are suggested in the literature. In this paper by using three level
H-bridge topology & five level cascaded multilevel inverter based DSTATCOM
the voltage sag is compensated effectively with reduced total harmonic
distortion (THD).
KEYWORDS:
1. Cascaded Multilevel Inverter
2. DSTATCOM
3. Power Quality
SOFTWARE: MATLAB/SIMULINK
CIRCUIT
DIAGRAMS:
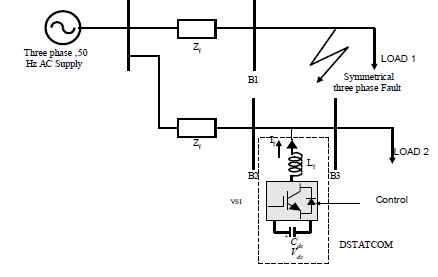
Fig. 1. Three-phase, 3-level H-bridge inverter based
DSTATCOM
Fig. 2. Three-phase, 5-level Cascaded H-bridge
inverter based DSTATCOM
BLOCK DIAGRAM:
Fig. 3. System Block Diagram
EXPECTED SIMULATION RESULTS:
Fig. 4(a) Sag At Bus B3 (b) Injected Current By
DSTATCOM (c) Compensated Voltage At Bus B3 (d)Active & Reactive Power At
Bus B3 (e) Injected Active & Reactive (f) Compensated Active & Reactive
Power at bus B3
Fig. 5 (a) Sag At Bus B3 (b) Injected Current By
DSTATCOM (c) Compensated Voltage At Bus B3 (d)Active & Reactive Power At
Bus B3 (e) Injected Active & Reactive (f) Compensated Active & Reactive
Power at bus B3
Fig. 6(a) Phase voltage & Line voltage for
3-level inverter based DSTATCOM (b) Phase voltage & Line voltage for
5-level inverter based DSTATCOM
CONCLUSION
The paper presents the principle of
operation of cascaded H-bridge converter and simulation studies on cascaded
converter based DSTATCOM using Sinusoidal PWM control. It is observed that the
DSTATCOM is capable of supplying the reactive power demanded by the load both
during steady state and transient operating conditions. The harmonics in
cascaded H-bridge five-level inverter current are less compared to three-level
inverter operating at same switching frequency.
REFERENCES
[1] M.
H. J. Bollen, Understanding Power
Quality Problems-Voltage Sags & Interruptions, New York, IEEE Press. 2000.
[2] R. C. Duggan, F. Mc. Granaghan, H. Wayne
Beaty, Electrical Power System Quality,
McGraw-Hill. 1996.
[3] Youn
Soo-Young, Jung, Tae-Hyun Kim, Seung-II Moon & Byung- Moon Han. “Analysis
and Control of DSTATCOM for Line Voltage Regulation” Power Engineering Society
Winter Meeting, vol. 2, no. 2, pp. 726-734, Jan. 2002.
[4] S. Iyer, A. Ghosh and A. Joshi, “Inverter
Topologies for DSTATCOM applications-A Simulation Study,” Elect. Power Syst. Res., vol. 75,
no.2/3, pp. 161-170, Aug. 2005.
[5] C.
A. Quinn, N. Mohan and H. Mehta, “Active Filtering of Harmonic Current in
Three-Phase, Four-wire systems with Three-Phase and Single-Phase non-linear
Loads,” Proc Appl. Power Electron.
Conf., 1992, pp.829-836.